While the year 2020 passing tough time due to pandemic situation, July 30th, 2020 – is the day appears with full of hope and excitement. This day NASA launches humanity’s most sophisticated rover for MARS, named Perseverance. Florida’s Cape Canaveral Air Force Station launched Rocket ULA Atlas-V at 11:50 UTC
MISSION OBJECTIVE
Looking for Habitability
Identify past environments capable of supporting microbial life.
Seeking Biosignatures
Seek signs of ancient life, particularly in special rocks known to preserve signs of life over time.
Caching Samples
Gather rock and soil samples that could be returned to Earth by a future NASA mission.
Preparing for Humans
Demonstrate technology for future robotic and human exploration.
Perseverance
Perseverance rover, built at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California, is loaded with scientific instruments, advanced computational capabilities for landing and other new systems. Perseverance [persistence in doing something despite difficulty or delay in achieving success] the name given by 13 years old boy from Virginia, Alexander Mather. Unlike previous missions Perseverance will not use solar panel, instead will use 45KG Radioisotope Thermoelectric Generator (RTG) that converts the heat of radioactive decay of plutonium into electricity. Also there is a pair of lithium ion batteries to help handle peak demands or when rover uses more energy than RTG produces. Curiosity also uses RTG and able to survive from dust storm.
| Launch mass | 1025 kg |
| Dimensions | 3 × 2.7 × 2.2 m |
| Power | 110 watts |
Instruments of Perseverance
Basically Perseverance has developed on the base architecture of previous rover, Curiosity. Shape is almost same, 126 KG heavier, instruments and wheels are upgraded and new instruments are integrated. Seven key instruments are discussed as follows
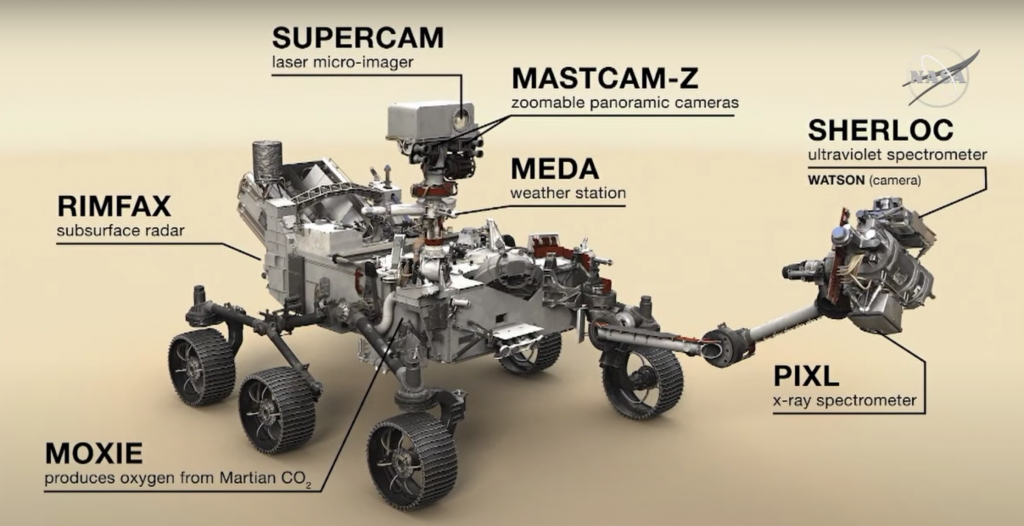
MEDA – Mars Environmental Dynamics Analyzer (Spain)
MEDA is a set of sensors to measure the temperature, wind speed & direction, wind pressure and relative humidity as well as dust size and shape.
This research will help to design shelters for astronauts living on mars.
RIMFAX – Radar Imager for Mars’ subsurface experiment (Norway)
Will research on geological structure of surface; like ground densities, structural layers, buried rocks, meteorites, and detect underground water or ice upto 10m depth. Ground penetrating on mars previously it was measured by orbiters.
MOXIE – Mars Oxygen ISRU Experiment
MARS’s atmosphere contains 96% CO2 MOXIE will convert CO2 to O2 This instrument will help to supply Oxygen to astronauts and eliminates the load of carrying extra Oxygen.
PIXL – Planetary Instrument for X-Ray Lithochemistry
An X-ray fluorescence spectrometer to determine the fine scale elemental composition of Martian surface materials. PIXL will provide capabilities that permit more detailed detection and analysis of chemical elements than ever before.
SHERLOC – Scanning Habitable Environments with Raman and Luminescence for Organics and Chemicals
An ultraviolet (UV) Raman spectrometer that uses fine-scale imaging and an ultraviolet laser to determine fine-scale mineralogy and detect organic compounds.
MASTCAM-Z
An advanced camera system with panoramic and stereoscopic imaging capability with the ability to zoom. This one is rover’s main camera will take color image and video HD.
SUPERCAM (France)
An instrument that can provide imaging, chemical composition analysis, and mineralogy. The instrument will also be able to detect the presence of organic compounds in rocks and regolith from a distance of 7m. SUPERCAM is the upgraded version of Curiosity’s Chem-cam.
Cameras & Microphones
This is first time ever microphones are integrated. Two Microphones are attached with this rover, one on the SUPERCAM and other on the landing package. Supercam mic will allow the scientists to hear the sound of Mars and other one allow engineers to capture the sound when rover works.
23 Cameras are attached with perseverance, some new and some are extended version from curiosity. Among them 9 will be used for engineering, 7 for scientific research and 7 will be used for entry-descent-landing stage and during working on Mars.
INGENUITY
Most exciting part of this mission is Perseverance rover carrying a Helicopter. This is the first time we will generate flight outside of Earth. Name of this Helicopter is INGENUITY[The quality of being clever, original, and inventive] Name has given by a student, Vaneeza Rupani of Northport, Alabama. Although in 1985 Soviet’s vega mission deployed 2 Helium (He) balloons in venus, transmitted data for 48 hrs
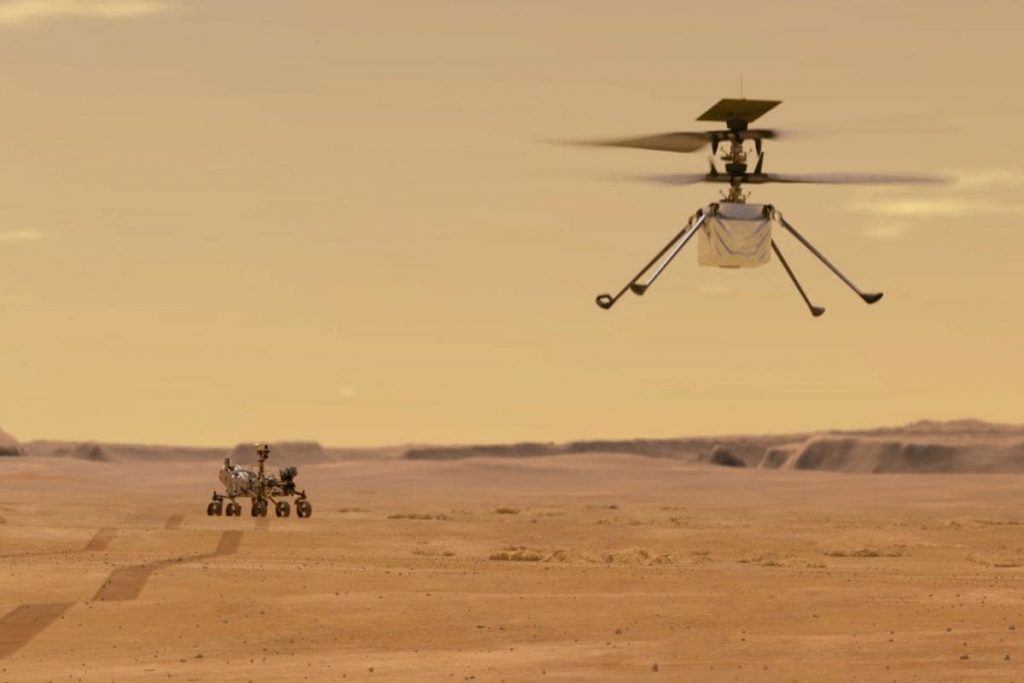

Though the gravity of Mars (38% of Earth) is an advantage to fly an object but the challenge is the atmospheric density which is only 1% of Earth. Scientists believe if the object is light enough and the blades spin fast enough then it should fly. INGENUITY contains two blades, each of 35gm. So 70gm blade able to carry 1800gm helicopter. While the blades spin around 2400 rpm which is 8 times faster than a normal helicopter at Earth. Consumed power 350 Watts.
A Solar panel has attached with this helicopter to charge the 273gm Battery (35–40 Wh (130–140 kJ). A full recharge needs one 1sol (1day in Mars), with fully charged helicopter can fly 90s with Max altitude of 5m. Only 1/3 of the battery energy will be used to fly other 2/3 will use to make warm the equipments, while the temperature goes below -100oC
LANDING PROCEDURE
In previous missions landing on planets used Airbag landing process. With this process its difficult to operate the landing at actual desired area. Rovers simply lands on the surface and it takes couple of days to drag them to the interest area.
This time landing will use Terrain relative landing process, which was also used successfully for Curiosity. Perseverance will add some amazing improvements on landing. In this process Perseverance can check the landing area and able to land on suitable place. Also Range Trigger can control when to open the parachute so Perseverance can land exact desired area.
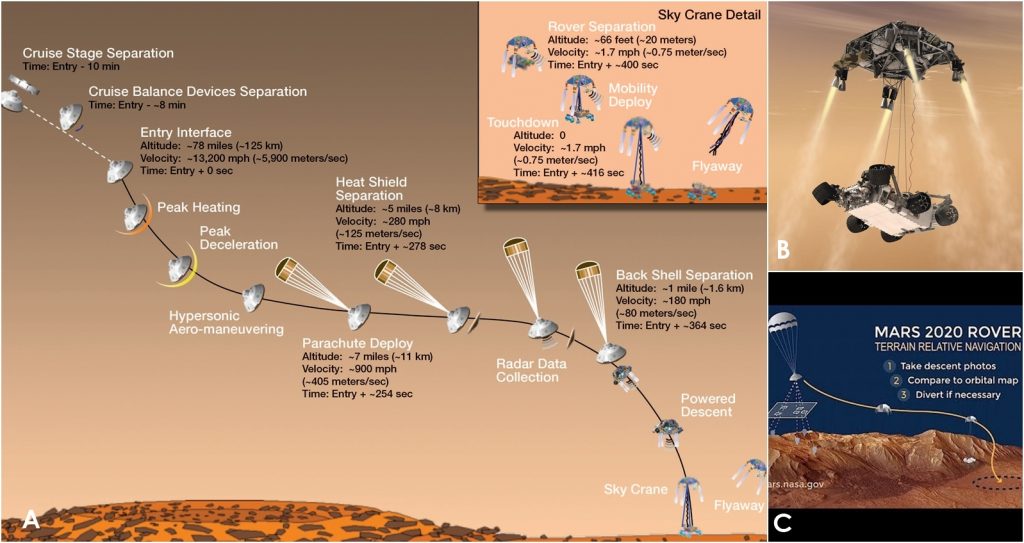
Landing has three stages Entry-Descent-Landing. Whole process takes 7mins to complete. This time also known as 7 minutes of terror. This is the most crucial time for any mission. When Object enters into the planet’s atmosphere then Entry interface started. During this time object takes very high speed almost 20,000Km/Hr. with this speed heat rises upto 2100oC. Heat shield protects the rover. After 2.5 min(approx) parachute opens and the speed comes down to 1,600Km/Hr. Then heat-shield became separated. When the rover comes near to the landing area sky-crane came out, which carries the rover. Above the landing area (21m height approx) rover came out with strings. Confirming the safe landing of the rover Sky-crane cut the string and fly away from that area and execute self-destruction.
JEZERO CRATER
MARS has two famous crater Gale Crater and Jezero Crater. Currently Curiosity exploring Gale Crater and Perseverance will explore Jezero Crater. Crater means a large bowl-shaped cavity in the ground which is typically caused by an explosion or the impact of a meteorite. In past when the planet was warm, there was flow of water, approximately 3.5 ~ 3.8 billion years back. That time Jazero Crater was full of water with input and output flow.

Why this area
One of the objectives of current MARS 2020 mission is “Seeking Biosignatures”. Scientists believe this area has high possibility of containing signs of ancient life. Reason behind this believe, if we have a close look at the crater, an input and output channel is visible on the crater (pic B). Usually in this situation a delta forms near the input channel. And Jezero Crater has same delta (pic C) which indicates the input channel. All these points have strong proof of having water, moreover flowing water on Mars. And where is water there is high possibility of life. Another point, flowing water may bring living things to the crater. Afterwards water disappeared from the carter leaving the ancient life inside. There are two ways to find ancient life: fossils or biosignature. On Mars there is high possibility of getting biosignature, if there was life.
SAMPLE RETURN
Another objective of Mars 2020 mission is gather rock and soil samples and return back to the Earth.

Perseverance is able to drill and collect sample of rocks or soils in a tube. As shown on pic A, circle marked areas are selected points to collect samples. these samples will be sealed inside a tube.
In future, NASA will conduct another mission, consists of a rover, lander and orbiter to collect those samples. Rover will receive the sample tubes and handover it to the lander. Lander will launch a rocket and pass them to the orbiter. Orbiter will push them towards Earth.
CONCLUSION
This mission, Mars 2020 risen the level of hope much higher. Future robotic or human missions will be highly influenced by the research results of Perseverance’s instruments like MOXIE, MEDA, INGENUITY etc. Whole world is eagerly waiting for the day 18th February, 2021.
*All information are taken from NASA official website.
One thought on “Mission MARS 2020”